2nd edition of EARTH Summit 2025
Context: Recently, the Union Home Minister inaugurated the EARTH Summit 2025 at Mahatma Mandir Convention & Exhibition Centre in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
More on the News
- The theme for Earth Summit 2025 is “Empowering Rural Innovation for Global Change.”
- More than thirteen digital cooperative services were launched under Sahakar Sarathi during the event.
- Gandhinagar edition of Earth Summit 2025 is the second in a planned series of three national summits aimed at creating a comprehensive rural development framework.
- The third summit in Delhi will present a unified national policy derived from discussions held across all three summits.
- The Hyderabad edition, which served as the first summit of the series and was held on 20–21 November, was designed as a policy-shaping platform to accelerate rural transformation.
Key Highlights of Earth Summit 2025
- The purpose of these summits is not only to strengthen the rural economy but also to rethink various aspects of rural development and derive result-oriented solutions.
- The edition brings together technology start-ups, cooperative federations, state governments, innovation networks, and multilateral development bodies (MDBs).
- The summit will explore how digital tools, AgriTech and RuralTech solutions can drive growth across rural sectors.
National Statistical Commission (NSC)
Context: Recently, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance has recommended granting full statutory authority to the National Statistical Commission (NSC) to improve data credibility, ensure uniform methodology, and address inconsistencies across India’s statistical ecosystem.
More on the News
- The standing committee submitted its report in the Lok Sabha, recommending that the National Statistical Commission should be given full statutory powers.
- The committee observed rising inconsistencies in datasets produced by government agencies and private firms.
- The panel recommended that the NSC should serve as the nodal and autonomous body for all core statistical activities.
- The committee highlighted the under-representation of India’s informal sector in macroeconomic indicators.
- The panel flagged issues of overlapping datasets released by multiple agencies and urged harmonisation.
- The committee emphasised the need for ethical and efficient adoption of Artificial Intelligence in the National Statistical System.
National Statistical Commission (NSC)
- The NSC of India is an autonomous body established in 2005 to improve the quality, credibility, and timeliness of official statistics
- The setting up of the NSC followed the decision of the Cabinet to accept the recommendations of the Rangarajan Commission, which reviewed the Indian Statistical System in 2001.
- Its headquarters are located in New Delhi.
Discriminatory Laws Against Persons with Leprosy
Context: Recently, the National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) submitted a report to the Supreme Court stating that nearly 97 Central and State laws still contain discriminatory provisions against persons affected by leprosy.
More on the News

- The NHRC has apprised the top court that India continues to account for about 57% of all reported leprosy cases worldwide.
- The NHRC recommended reforms for early detection, timely treatment, rehabilitation and removal of all discriminatory clauses in laws.
- Petitioners including the Federation of Leprosy Organisation and Vidhi Centre for Legal Policy argued that old legal provisions have no relevance after modern medical advances.
- The Supreme Court asked all States and Union Territories to submit reports on actions taken based on NHRC’s recommendations.
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
- NHRC of India was established in 1993 under the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993 as amended by the Protection of Human Rights (Amendment) Act, 2006.
- The commission is the watchdog of human rights in the country, that is, the rights relating to life, liberty, equality and dignity of the individual guaranteed by the Constitution.
- The Commission consists of a chairperson, five full-time Members and seven deemed Members.
- The Chairperson and Members of the Commission are appointed by the President of India based on the recommendations of a committee chaired by the Prime Minister.
Domestic Systemically Important Banks ("D-SIBs")
Context: Recently, the Reserve Bank of India released its 2025 list of systemically important banks to strengthen financial stability.
More on the News
- The RBI has identified State Bank of India, HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank as Domestic Systemically Important Banks for 2025.
- These three banks, continue under the same systemic importance buckets assigned in the previous year.
- The RBI has set additional Common Equity Tier 1 requirements for each bank based on its Risk Weighted Assets.
- The D-SIB framework requires annual disclosure of the banks’ names and their assigned buckets according to Systemic Importance Scores.
- It explains that the current classification is based on the financial data submitted by banks as of March 31, 2025.
Domestic Systemically Important Banks
- These are institutions considered "Too Big To Fail" (TBTF) within a domestic economy because their potential failure could significantly disrupt the entire financial system and the broader economy.
- In India, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the authority responsible for identifying and supervising D-SIBs, following a framework introduced in 2014.
Numaligarh Refinery accorded Navaratna status
Context: Recently, the Union Minister for Petroleum and Natural Gas announced that Numaligarh Refinery Limited has been granted Navratna status, making it the 27th Central Public Sector Enterprise to receive this designation.
More on the News
- The recognition highlights NRL’s strong financial performance and its expansion projects, including the Numaligarh Refinery Expansion Project (NREP) and the bamboo-based 2G bioethanol plant.
- NRL operates a 3 million metric tonnes per annum (MMTPA) refinery in Assam and posted a turnover of ₹25,147 crore and net profit of ₹1,608 crore in FY 2024-25.
- The enterprise reported robust financial performance with a turnover exceeding ₹25,000 crore and significant net profits in FY 2024-25.
- The Navratna status is expected to support NRL’s future expansion, operational flexibility, and investment capability.
Navratnas Status
- It is the second category of the central government-owned ‘Ratna’ companies, placed between the Maharatnas and the Miniratnas, based on criteria including profitability, net worth, earnings, inter-sectoral performance, etc.
Eligibility Criteria
- Must already be a Miniratna I, Schedule ‘A’ CPSE and have obtained an ‘excellent’ or ‘very good’ MoU rating in three of the last five years
- It should have a composite score of 60 or more in six performance indicators like profitability, productivity, efficiency, etc
- Financial Autonomy: Companies can invest up to ₹1,000 crore, or 15% of their net worth, in a single project without prior government approval, provided the total annual investment does not exceed 30% of their net worth.
Exercise Harimau Shakti
Context: India and Malaysia began the fifth edition of their joint military exercise, Harimau Shakti, at the Mahajan Field Firing Range in Rajasthan.
More on the News
- The exercise will run from December 5 to 18 and is aimed at enhancing interoperability in sub-conventional operations under the UN Chapter VII mandate.
- The Indian Army is represented primarily by troops from the Dogra Regiment, while the Malaysian contingent comprises personnel from the 25th Battalion of the Royal Malaysian Army.
- The two sides will train together in counter-terrorist operations, including cordon-and-search drills, search-and-destroy missions, and heliborne operations.
- The curriculum also includes Army Martial Arts Routine, combat reflex shooting and the yoga sessions.
- The focus will be on improving joint responses, reducing operational risks and aligning drills with UN peacekeeping requirements.
- It is an annual training event conducted alternatively in India and Malaysia.
- The first edition was conducted in 2018 in the forests of Sengai Perdik, Hulu Langat, Malaysia.
Road Accident Death Toll Rising
Context: Recently,theUnion Minister of Road Transport and Highways informed that the number of road accident fatalities in India rose by 2.3 percent.
More on the News
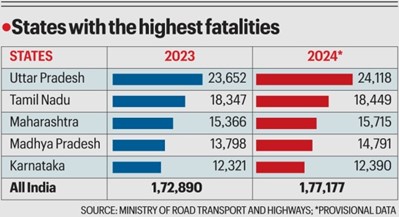
- India recorded 4.8 lakh accidents in 2023, leaving 1.7 lakh dead and 4.6 lakh injured, resulting in the death of 485 persons every day.
- In 2024, Uttar Pradesh had the highest accident-to-fatality ratio at 52.37%, meaning every second road accident was fatal.
- The data is based on real-time information entered by state police on the government’s Electronic Detailed Accident Report (e-DAR) portal.
- Stockholm Declaration on Road Safety, India adopted at the 3rd Global Ministerial Conference in February 2020, sets a global target of reducing road traffic deaths and injuries by 50% by 2030.
- The UN General Assembly adopted a resolution launching the Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021–2030 with a target to reduce road traffic deaths and injuries by at least 50% by 2030.
- As reported in the World Road Statistics2024, the road-fatality rate per lakh population stands at 4.3 in China, 12.76 in the USA, and 11.89 in India.
- To reduce accidents and fatalities, the government has adopted a road safety strategy based on the “4Es” — education, engineering, enforcement, and emergency care.
- Funds allocated for road safety range from 2.21% to 15% of the total cost of National Highway development projects, depending on the structures involved.
About e-DAR Portal
- It is an initiative of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH), Government of India and is funded by the World Bank.
- The project aims to improve road safety in the country.
- Main objective: Development of the Integrated Road Accident Database (iRAD) to enrich accident data from all parts of India





