You're all caught up—no notifications available.
Explore All Exams at KGS

All Exams
Explore All Exams at KGS
Khan Sir Courses
Geography I Polity I History | World Map I Indian Map I Economics I Biology
UPSC & State PSC
UPSC I BPSC I UP-PSC I MP-PSC
State Exams
UP I Bihar I MP | Rajasthan
NEET | JEE | CUET | Boards
NEET | JEE | CUET | Boards
Defence Exams
NDA I CDS I CAPF I AFCAT I SSB I Agniveer
Police Exams
UP SI | Bihar SI | Delhi Police | UP Constable
SSC Exams
CGL I CPO I CHSL I MTS I SSC GD I Delhi Police
Foundation Courses
Physics I Chemistry I Biology I History I Geography I Polity I NCERT I Math I English | Map I Reasoning
Railway Exams
RRB | RPF
Teaching Exams
TET | Teaching | UGC
Banking Exams
SBI | RBI | IBPS
Engineering Exams
Civil | Electrical | Mechanical
UGC NET
UGC NET/JRF
Current Affairs provides you with the best compilation of the Daily Current Affairs taking place across the globe: National, International, Sports, Science and Technology, Banking, Economy, Agreement, Appointments, Ranks, and Report and General Studies

SYLLABUS
GS-2: Important International Institutions, agencies and fora - their Structure, Mandate.
Context: As per the Least Developed Countries Report 2025, released by the UNCTAD, services now account for nearly half of economic output across LDCs, yet this growth has not led to significant gains in productivity, incomes, or inclusive development.
More on the News
• The Report released by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) examines structural transformation, employment, and productivity trends in the least developed countries (LDCs).
• It underscores that employment generation, especially quality employment, has emerged as the central development constraint for LDCs over the coming decades.
• The report situates this trend within: Weak industrialisation, Persistent informality in labour markets, Limited integration into global value chains.
Key Findings of the Report
• Services-led Growth without Transformation:
o Despite the growing role of services, average per capita growth in LDCs remained weak in 2024, underscoring a widening gap between job creation and decent work.
o Labour productivity in the average LDC is around 11 times lower than in the median developed economy, constraining the kinds of services that can be produced and exported.
• Jobs versus Decent Work:
o LDCs must create about 13.2 million jobs annually until 2050 to absorb new labour market entrants, making employment creation a central development constraint.
o While services have absorbed much of this labour, employment is dominated by informal retail, personal services and subsistence work, so working poverty remains widespread and the gap between “more jobs” and “better jobs” is widening.
• Weak Structural Linkages: Services expansion is poorly connected to manufacturing, exports, and technological upgrading.
o Without forward and backward linkages, services-led growth risks deepening marginalisation.
• Deep Digital and Gender Divides: Across LDCs, women are about 42% less likely than men to use mobile internet, and rural residents are 50% less likely to be connected than urban residents.
o These disparities restrict access to higher-productivity service jobs, reinforcing inequality.
Recommendations of the Report
• No Shortcut to Development: UNCTAD concludes that services led growth is not a shortcut to development. Services can underpin development only if they raise productivity, deepen links to agriculture and manufacturing, and are backed by investments in infrastructure, energy, education and skills.
• Close Skills and Digital Divides: Invest in universal, affordable connectivity, particularly in rural areas, and promote gender inclusive digital access
o Scale up training in digital and soft skills, support local innovation hubs, and integrate digital literacy into education systems to enable a shift into higher productivity services.
• Strengthen Structural Transformation: The governments should upgrade traditional services (retail, transport, tourism) through quality standards, better infrastructure, and SME support so they can generate decent work and local linkages.
About Least Developed Countries (LDCs)
• LDCs are a group of low-income nations identified by the United Nations based on three criteria: low per-capita income, weak human assets (health, education, nutrition), and high economic vulnerability to shocks such as climate change or commodity dependence.
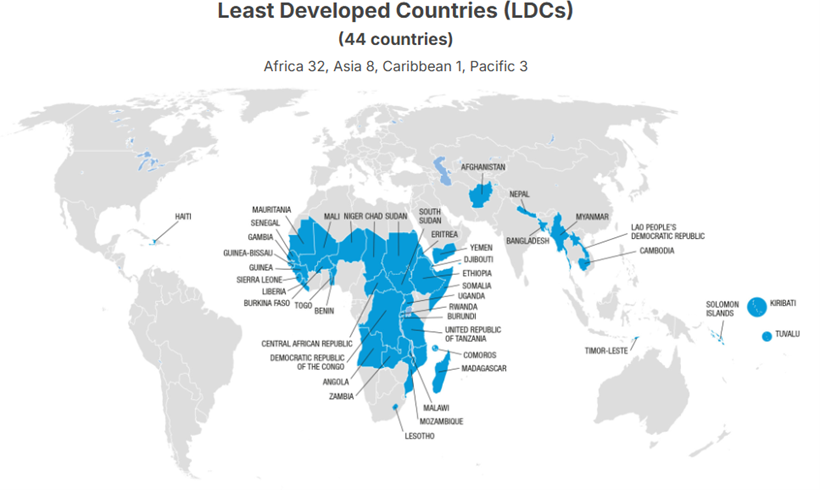
• There are currently 44 economies designated by the United Nations as LDCs, entitling them to preferential market access, aid, special technical assistance, and capacity-building on technology, among other concessions.
• The highest concentration is in Africa (32), followed by Asia (8).
• As of early 2026, eight countries have graduated from the LDC category since it was established in 1971 by the UN General Assembly (UNGA).
About the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
• The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) is a permanent intergovernmental body of the United Nations, established in 1964 by the UNGA.
• Its primary goal is to promote the integration of developing countries, especially Least Developed Countries (LDCs), into the global economy through fair trade, investment, finance, and technology policies.
• The major flagship reports of UNCTAD are: Trade and Development Report, World Investment Report, Technology and Innovation Report, and Least Developed Countries Report.
• It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
Sources
Down To Earth
Unctad

Course Related Query:
Ask Your DoubtsStore Related Query:[email protected]NCERT Books
Resources
We love learning. Through our innovative solutions, we encourage ourselves, our teams, and our Students to grow. We welcome and look for diverse perspectives and opinions because they enhance our decisions. We strive to understand the big picture and how we contribute to the company’s objectives. We approach challenges with optimism and harness the power of teamwork to accomplish our goals. These aren’t just pretty words to post on the office wall. This is who we are. It’s how we work. And it’s how we approach every interaction with each other and our Students.
Come with an open mind, hungry to learn, and you’ll experience unmatched personal and professional growth, a world of different backgrounds and perspectives, and the freedom to be you—every day. We strive to build and sustain diverse teams and foster a culture of belonging. Creating an inclusive environment where every students feels welcome, appreciated, and heard gives us something to feel (really) good about.
Get Free academic Counseling & Course Details
